Using Ransac to Segment Points and/or Remove Outliers
Often it is helpful to segment points and one way to identify the floor for a robot or the road for a car is by using Random Sample Consensus (RANSAC). RANSAC is suprisingly simple and effective if most of your data points are along the same line or plane e.g., a mostly empty room.
First, I’ll start out with a simple 2d example, and then I’ll briefly talk about a 3d version.
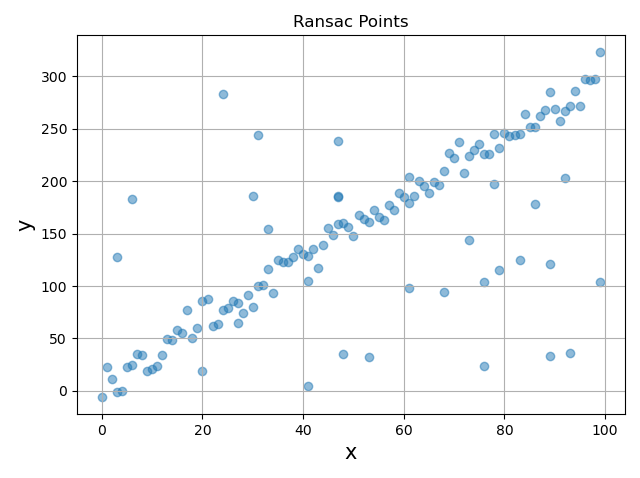
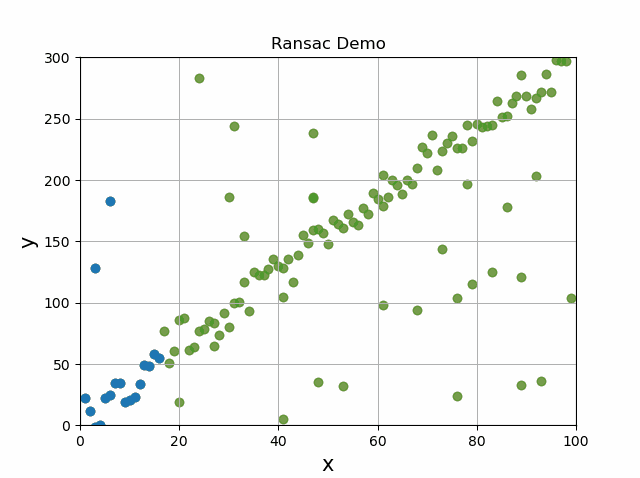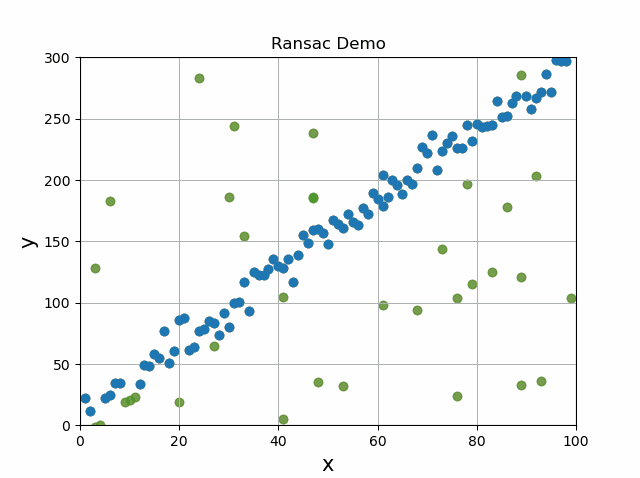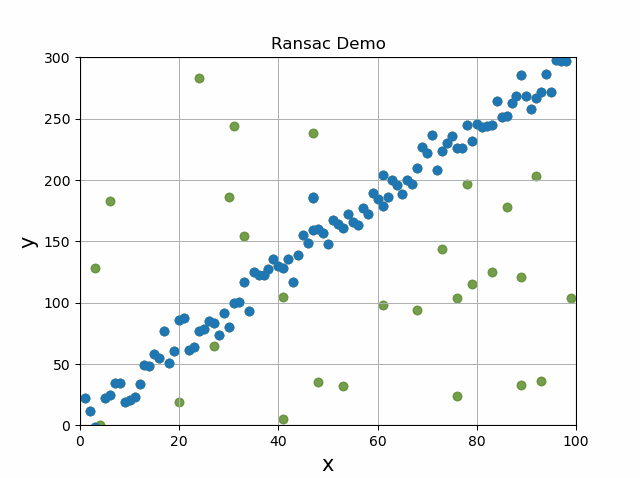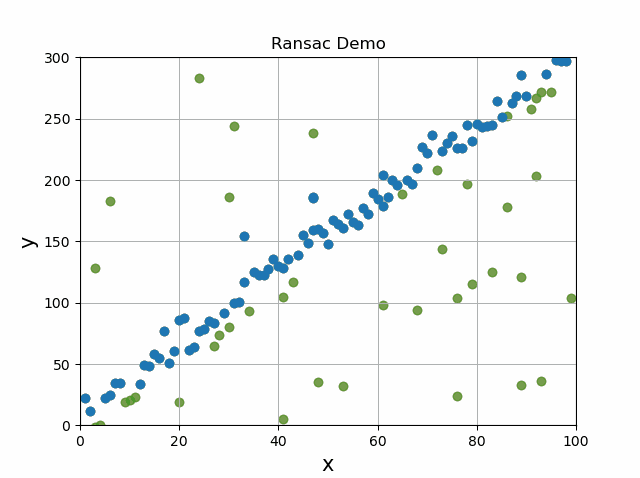
In the above image labeled Ransac Points, we can see that most of the points are along a straight line with a smattering of outliers. If we want to seperate the two groups of points into an inlier and an outlier groups, we can use the following RANSAC steps.
For n iterations:
- Select two random points from all the points to draw a line (2d case)
- Measure the distance of the remaining points to the line
- In a new list, keep points found within a specified distance
- If more points were currently found than during all previous iterations, save the best line and points
Return best line and resulting points.

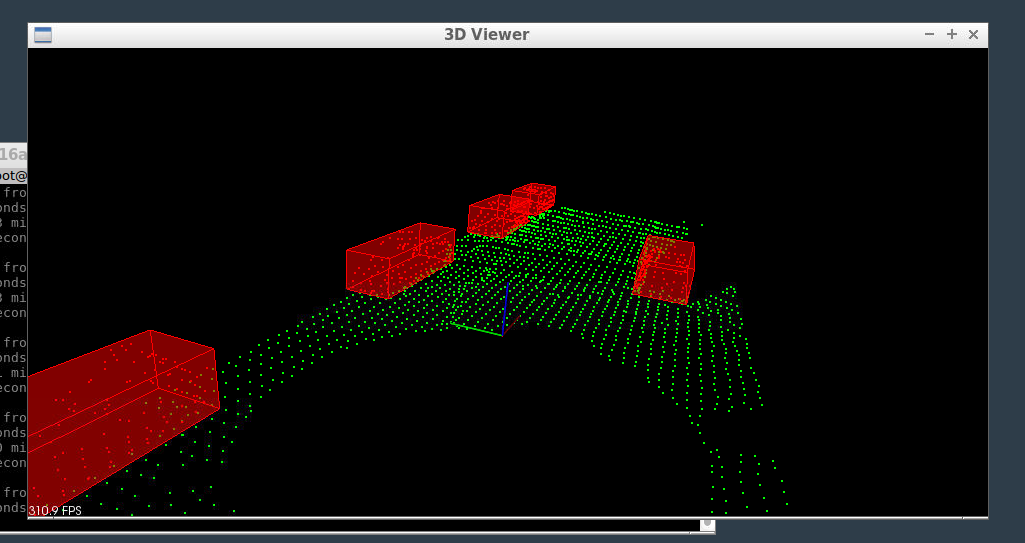
Now if you use this same algorithm but change it to measure the distance of points from a 3d plane, then you can segment the road as shown below. The green points are the road, and the red are the cars on the road.
You can see the python code for this project here, and my 3d implementation of RANSAC in C++ here.
RANSAC has some other cool applications we may explore at another time such as stitching pictures together, but for now I hope this simple algorithm inspires you. You often don’t need fancy algorithms or black box models to perform tasks such as the one shown above.
Cheers